Laparoscopy: Radical Cystectomy
Bladder tumor is the most common tumor in the genitourinary system, accounting for more than 60%, most of which are epithelial tumors, accounting for more than 95%. Transitional cell tumor is the most common epithelial tumor of the bladder, accounting for more than 80%, squamous cell carcinoma accounts for 3% ~ 6.7% and adenocarcinoma accounts for 0.5% ~ 2.6%.
Most of the transitional cell tumors of the bladder are transitional cell carcinoma, and a few are benign papilloma, but they are easy to relapse and can become cancerous.
The bladder is a muscular cystic organ that stores urine. When empty, it is in the shape of a triangular pyramid. The top is thin and pointed. It is called the bladder tip, and the median umbilical ligament is connected to the umbilicus. The bottom is triangular. It is called the bottom of the bladder, and the most part between the tip and the bottom is called the bladder body.
The lower part of the bladder becomes thinner, which is called the bladder neck. In men, it is in contact with the prostate. The area between the left and right ureteral orifices and the internal orifices of the urethra is called the bladder triangle.
Indications
1. T2-t4a, n0-x, M0 invasive bladder cancer;
2. High risk non muscle invasive bladder cancer T1G3 (high grade);
3. Tis that failed to be treated with BCG;
4. Recurrent non muscle invasive bladder cancer;
5. Extensive papillary lesions beyond the control of transurethral resection and bladder perfusion and bladder non urothelial carcinoma.
Things to note for laparoscopic radical cystectomy: for male
Laparoscopic cystectomy, step by step, don’t panic
Put your head low and your feet high, and try to put your intestines into the abdominal cavity
Free left and right ureters to protect blood supply
Umbilical artery, easy to find, early treatment, less bleeding
Lift up the vas deferens of the seminal vesicle and open the Di’s fascia
Only when fat is seen can it be separated to ensure that there is no problem with the rectum
Open the internal pelvic fascia and “8” suture DVC
Lateral ligaments, slow processing, hidden secrets
Please protect your sexual nerves and get a good reputation as a doctor
The urethra closes and then disconnects, and the bladder is placed in the abdominal cavity
Pelvic lymphadenectomy, vascular and neuroskeletal exposure
Total cystectomy is very complicated, and the clear steps are nothing
Learn more, practice more, make up a pithy formula and remember it
Things to note for laparoscopic radical cystectomy: for female
Female whole bladder, different form
Either one pot, or move forward
The suspensory ligament of ovary was cut first, and then the vaginal vault was opened
Lateral ligaments, slow processing, there are also small Secrets
Go round to the front and cut the urethra. The bladder and uterus are all down
If you only cut the bladder, do not hurt the reproductive blood supply
There is a space between the bladder and uterus, and the neck mouth is used to judge the water sac
For good in situ urinary control, the urethra is kept long enough
The specimen can come out of the vagina and make a bladder in the abdominal cavity
Mature anatomy, calm down, female operation is easier
The patient recovered quickly, healthy and beautiful
Total cystectomy involves the removal of the bladder, prostate and seminal vesicle in men and the removal of the bladder and urethra in women. Radical total cystectomy is the removal of bladder, prostate, seminal vesicle, pelvic peritoneum, pelvic lateral wall and surrounding tissues of blood vessels (including lymph nodes and lymphatic vessels) as a whole.
For women, it also includes the broad ligament, uterus, cervix and part of vagina.
Anesthesia: general anesthesia, endotracheal intubation
Position:
1. Cystoscopy was performed at the position of bladder lithotomy.
2. 20-30 ° head low and feet high. The instrument is between the two legs of the patient. Remove the head plate, place a rectangular soft pad under the legs, and place a shaft type self-made pad at the leg socket. The sacrum and tail are at the fork of the leg plate, and place a decompression Pad + birth pad. The two lower limbs are slightly separated. Cover the dressing, wrap the bandage, fix the legs. The head is padded with a head ring with a gel.
The hands are wrapped on both sides of the body, and the liquid is on the right hand. The anesthesia head frame shall be used, the square tape on the nipple shall be fixed, and the shoulder shall be provided with shoulder support and small square sponge pad to prevent the patient from sliding towards the head when the head is low and the foot is high. Equipment nurse’s articles preparation
Equipment nurse’s articles preparation
Emergency kit, endoscopic instrument kit, lens, 24 surgical routines, 8 microscopes, sterile lampshade, surgical gown *2, accessory kit *1, green large hole, small tablecloth, surgical towel
Plastic cavity mirror pliers (green latch, attractor, non-destructive injury pliers, bipolar + wire, cavity mirror scissors, trefoil pliers,)
Electric hook wire, green, purple, gold lock clip, titanium clip (in extra amount)
Several gloves, aspirator tube *3, ablation electrode, blood transfusion device, infusion set, application of indwelling needle (red), 1, 4 and 7 mousse suture, 45*30 protective film, endoscope protective sleeve *5, wound dressing medium *2, small *4, 20ml syringe, 50ml syringe, 11, 10 and 22 blades,
9*28 triangular needle, yellow catheter, 16 catheter (stage catheterization, intraoperative removal), several urine bags, PDS suture, 2-0 barbed wire, 4-0, 5-0 antibacterial vicho, developing small gauze *2, ordinary large gauze, oil gauze strip, 12.5 and 5.5 puncture apparatus, (with five puncture points) fluid membrane, 36cm ultrasonic scalpel, zebra guide wire, J-type ureteral catheter
Instrument preparation:
camera system, electric knife and ultrasonic knife
Ultrasonic scalpel patient right, bipolar and electrosurgical scalpel patient left, aspirator patient left shoulder
Personnel station:
At the beginning of the operation, the bed is lowered to the lowest level, and the head is low and the feet are high.
The main knife station is on the patient’s left, the first assistant is on the patient’s right, the mirror holder is on the patient’s head, the instrument nurse is on the left side of the main knife, the patient’s left hip is made into a cloth pocket to store instruments, and the instrument table is under the patient’s left foot (a small sterile table can be added with a tray)
Brief surgical procedures:
1. disinfect, lay sheets, connect various light source lines and electrocoagulation lines, establish pneumoperitoneum, explore the abdominal cavity, and place puncture apparatus.
Placement position of puncture device
Lens hole a: 10mm puncture device at the upper edge of umbilicus
Operating hole B: 12mm puncture device at McIntosh point
Operating hole C: 12mm puncture device with reverse Michaelis point
Operation hole D: insert a 12mm puncture device 3cm inside the left anterior superior iliac spine
2. Free ureter and clean up bilateral pelvic lymph nodes: open the retroperitoneum at the place where the ureter crosses the iliac vessels, free the ureter from the inner side of the external iliac artery to the entrance of the bladder, free and remove the left and right internal and external iliac lymph nodes and obturator lymph nodes with non-invasive grasping forceps and ultrasonic scalpels, and take them out with stone forceps.
3. free both sides and bottom walls of the bladder, free bilateral vas deferens and seminal vesicles, disconnect the vas deferens, separate the bottom of the bladder, enter the Diehl space, and push the rectum downward until the tip of the prostate.
4. free the lateral bladder ligament and prostate ligament, disconnect the urethra, and remove the prostate: disconnect with a super knife, cut the peritoneum at the top of the bladder to the anterior space of the prostate behind the pubis, open the pelvic floor fascia, free the tip of the prostate, suture the dorsal penis vein complex with 2-0 barbed wire, disconnect the tip of the anterior gland and the urethra, and completely remove the whole bladder.
5. specimen removal: make a subumbilical incision, cut each layer of abdominal wall longitudinally into the abdominal cavity, and take out the resected whole bladder. After taking out the specimen, wash it with warm sterilized water, keep the head high and the feet for 5 minutes, and suck it up. (one is to keep the perfusion solution for a few minutes for washing the pelvic floor, and the other is to slow down the blood circulation of the head.)
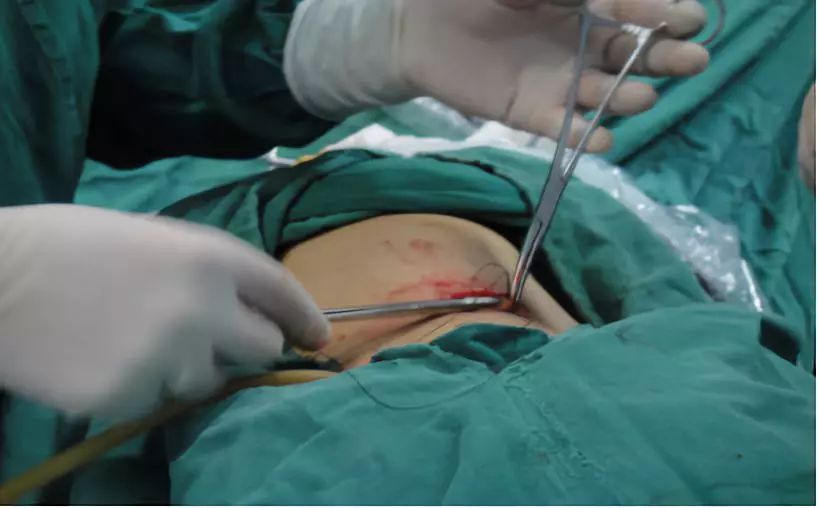
6. abdominal ureterostomy: free the sigmoid mesocolon, pass the left ureter behind the sigmoid colon, insert F7 single J tube into both ureters, and fix the ostomy with 0/5 buckwheat thread.
7. count the items and suture the incision: place the latex tube in the pelvic cavity, count the instruments and gauze, and suture the incision.
Thanks for reading, we hope you have enjoyed the content.
If you are looking for the endoscopy equipment, feel free to check our product page or contact us at our contact page.




Leave a Reply
Want to join the discussion?Feel free to contribute!